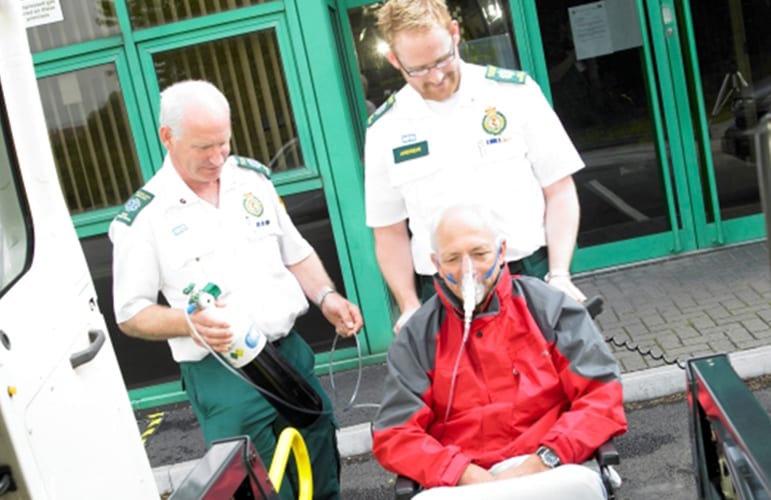
International media coverage for research linking flu vaccine with reduced risk of stroke
A study from CaHRU, ‘Influenza vaccination and risk of stroke: self-controlled case-series study‘, recently published in the journal Vaccine, received international coverage in news media. The study of almost 18,000 patients with stroke looked at data from general practices in Continue reading International media coverage for research linking flu vaccine with reduced risk of stroke


